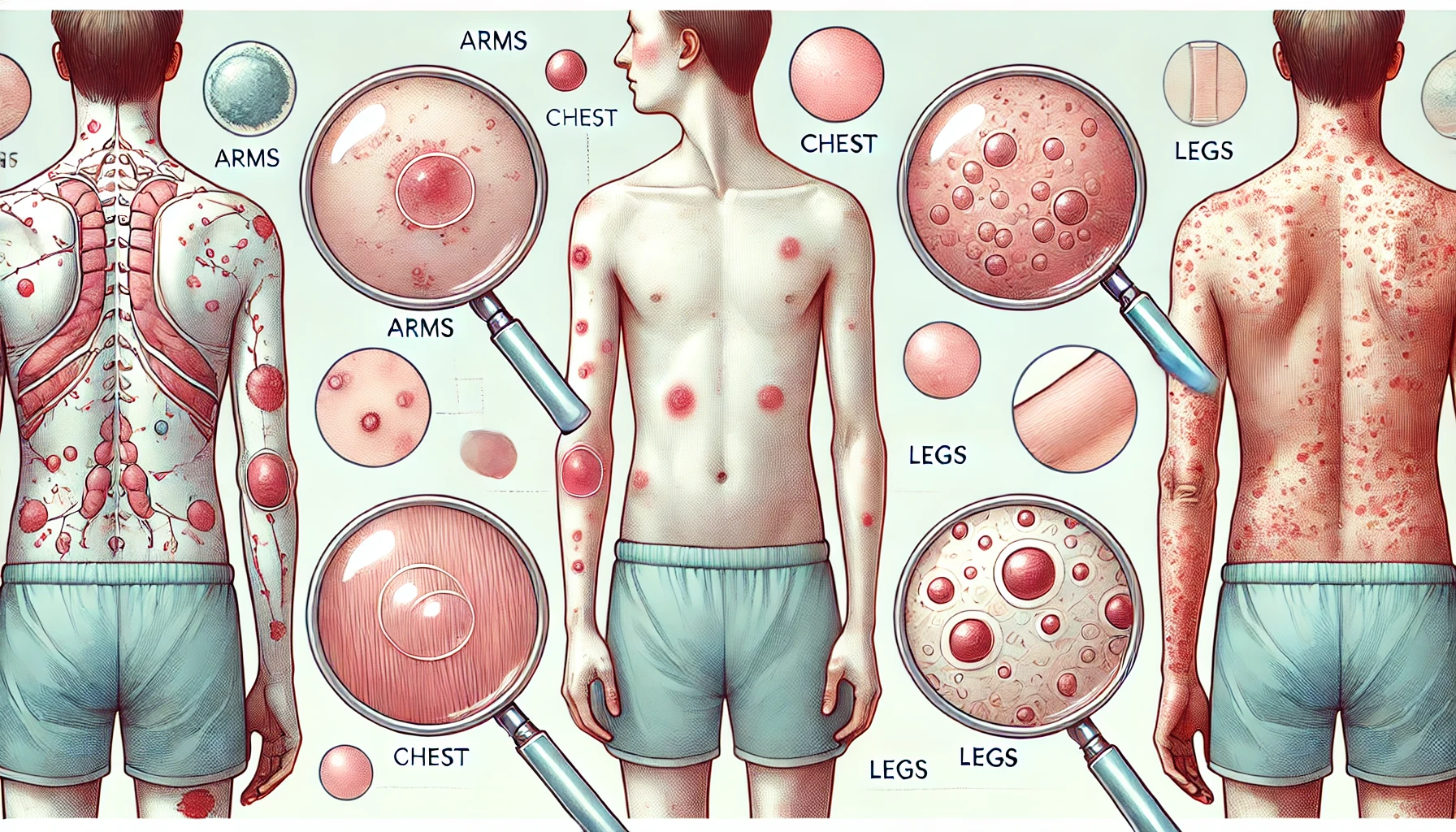
Check out this answer from Consensus: Rashes can be caused by a wide range of factors, including infections, medications, allergies, and mechanical irritation. Early recognition and appropriate management are crucial in treating rashes effectively and preventing complications. Healthcare providers must stay informed about the latest treatment options and guidelines to provide the best care for their patients.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of rashes, their types, causes, and management strategies.
Types of Rashes
Rashes can be categorized based on their appearance and underlying causes. The main types include:
1. Maculopapular Rashes
Maculopapular rashes are characterized by flat, red areas covered with small confluent bumps. They are commonly seen in viral infections such as measles, rubella, and roseola infantum 1 3.
2. Vesicular Rashes
Vesicular rashes present as small, fluid-filled blisters. They are often associated with viral infections like chickenpox and herpes simplex virus 2 4.
3. Petechial Rashes
Petechial rashes are small, red or purple spots caused by bleeding under the skin. They can be a sign of serious conditions such as meningococcal disease or other bacterial infections 2 6.
4. Erythematous Rashes
Erythematous rashes are red and inflamed, often resulting from allergic reactions or infections. Conditions like scarlet fever and drug reactions can cause erythematous rashes 2 7.
5. Urticarial Rashes
Urticarial rashes, also known as hives, are raised, itchy welts that can result from allergic reactions, infections, or other triggers 2 5.
Common Causes of Rashes
Rashes can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, allergies, and environmental exposures. Some of the most common causes are:
1. Viral Infections
Viruses are a leading cause of rashes, especially in children. Common viral infections that cause rashes include measles, rubella, roseola, and hand-foot-and-mouth disease 1 3 10.
2. Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections such as scarlet fever, impetigo, and meningococcal disease can also cause rashes. These rashes often require prompt medical attention due to their potential severity 1 4 6.
3. Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or environmental factors can result in rashes. Urticaria and contact dermatitis are common allergic rashes 3 9.
4. Drug Reactions
Certain medications can cause rashes as a side effect. Drug-induced rashes can range from mild to severe and may require discontinuation of the offending drug 1 10.
5. Mechanical Causes
Athletes and individuals exposed to friction or tight-fitting equipment may develop mechanical rashes. These rashes are often seen in sports settings and require appropriate management to prevent complications 4.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing the cause of a rash involves a thorough clinical history and physical examination. Key factors to consider include the appearance of the rash, associated symptoms, recent exposures, and medical history 2 6 8.
1. Clinical History
A detailed history can provide clues to the underlying cause of the rash. Important aspects to inquire about include recent travel, medication use, exposure to allergens, and vaccination status 6 8.
2. Physical Examination
A careful examination of the rash’s characteristics, distribution, and progression is essential. This helps in differentiating between various types of rashes and identifying potential causes 2 6.
3. Laboratory Tests
In some cases, laboratory tests such as blood tests, skin biopsies, or serological assays may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. These tests can help identify infectious agents or allergic triggers 10.
4. Treatment
Treatment of rashes depends on the underlying cause. Viral rashes often resolve on their own, while bacterial infections may require antibiotics. Allergic rashes can be managed with antihistamines and corticosteroids. It is important to avoid known triggers and follow medical advice for specific conditions 1 4 10.
Rashes are a common dermatological issue with a wide range of causes and presentations. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for effective treatment. By understanding the various types of rashes and their management strategies, healthcare providers can better diagnose, treat, and prevent these common dermatological issues.